Learn Spring Security
Contents
Role Based Authorization
So far we are allowed to access any APIs once authenticated successfully. But there are APIs which are supposed to be accessed only by users having specific roles. In the last two chapters, we accessed one of the ADMIN APIs - ListStudents - using Bob who does not have ADMIN role. In this chapter we will fix it by applying role-based authorization to secure the below APIs.
| API | Authorization |
|---|---|
| List Students | Admin can only view the list of students |
| List Instructors | Admin can only view the list of instructors |
| Create Course | Instructors can only create a new course |
Apply role-based restrictions with hasRole()
First let's add the above API urls in the SecurityConstants class like below:
public static final String API_LIST_STUDENTS = "/api/v1/users/students";
public static final String API_LIST_INSTRUCTORS = "/api/v1/users/instructors";
public static final String API_CREATE_COURSES = "/api/v1/courses";
We can apply customised restrictions to specific urls using antMatchers() in HttpSecurity configuration. Here we want to apply role-based restrictions which can be achieved using hasRole() with appropriate RoleEnum instance for the above urls as below:
@Configuration
public class ApiSecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain apiFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests(auth -> auth
.antMatchers(GET, PUBLIC_API_LIST).permitAll()
.antMatchers(API_LIST_STUDENTS, API_LIST_INSTRUCTORS).hasRole(ADMIN.name())
.antMatchers(POST, API_CREATE_COURSES).hasRole(INSTRUCTOR.name())
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.httpBasic();
return http.build();
}
}
As ListCourses and CreateCourse endpoints are the same but with different HttpMethod, we have to specify HttpMethod.POST in the antMatchers for CreateCourse API.
Restart the application and send a GET request to the ListStudents API using Admin user. Though we have secured this API for ADMIN role, we will get 403 Forbidden error. This is because Spring Security has no idea who has the ADMIN role, as we have not yet mapped the roles for any users while creating the list of UserDetails object.
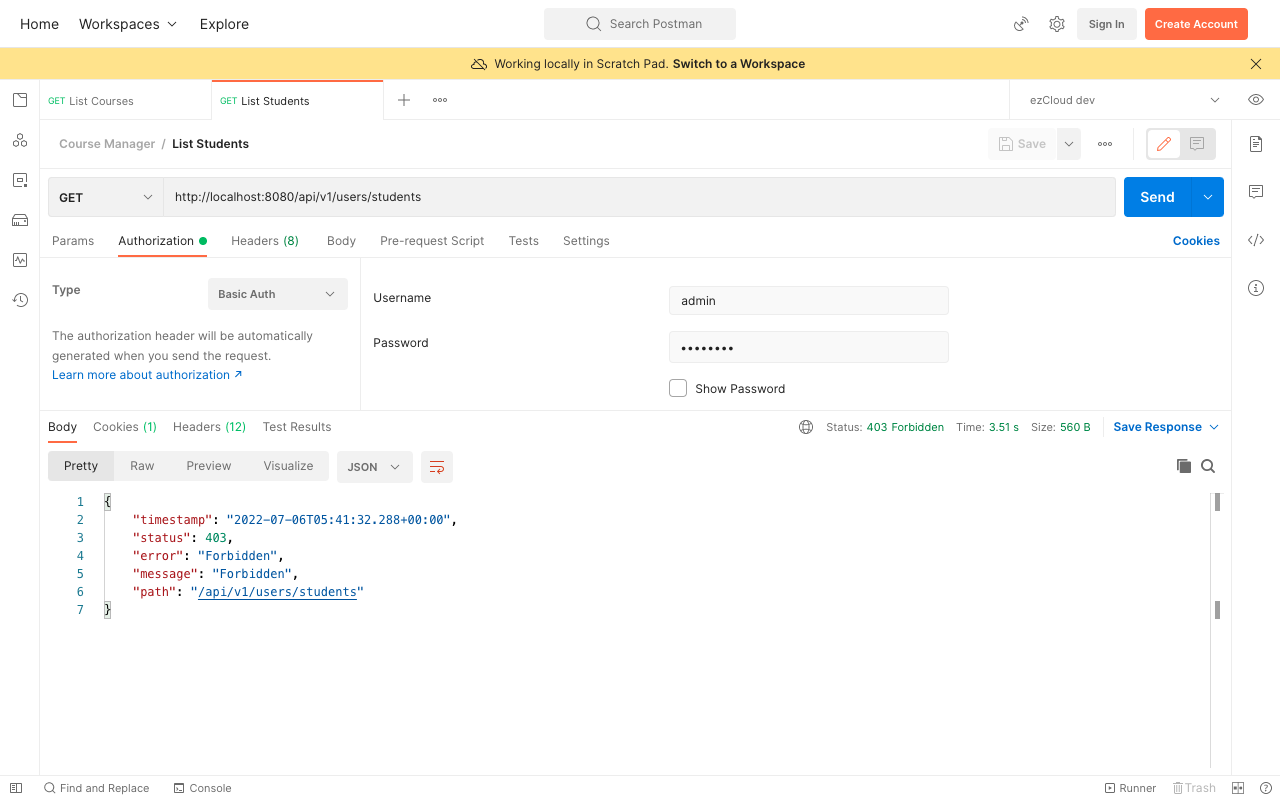
Update UserDetails with Roles
We can use roles() method in UserBuilder class to map the roles from AppUser. It is an overloaded method, here we chose the one which accepts String[]
public List<UserDetails> getAllUserDetails() {
return appUserRepository.findAll()
.stream()
.map(appUser -> User.builder()
.username(appUser.getUsername())
.password(appUser.getPassword())
.authorities(Collections.EMPTY_SET)
.roles(this.getRoles(appUser.getRoles()))
.build()
)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
private String[] getRoles(Set<AppRole> roles) {
return roles.stream()
.map(role -> role.getName().name())
.collect(Collectors.toSet())
.toArray(new String[0]);
}
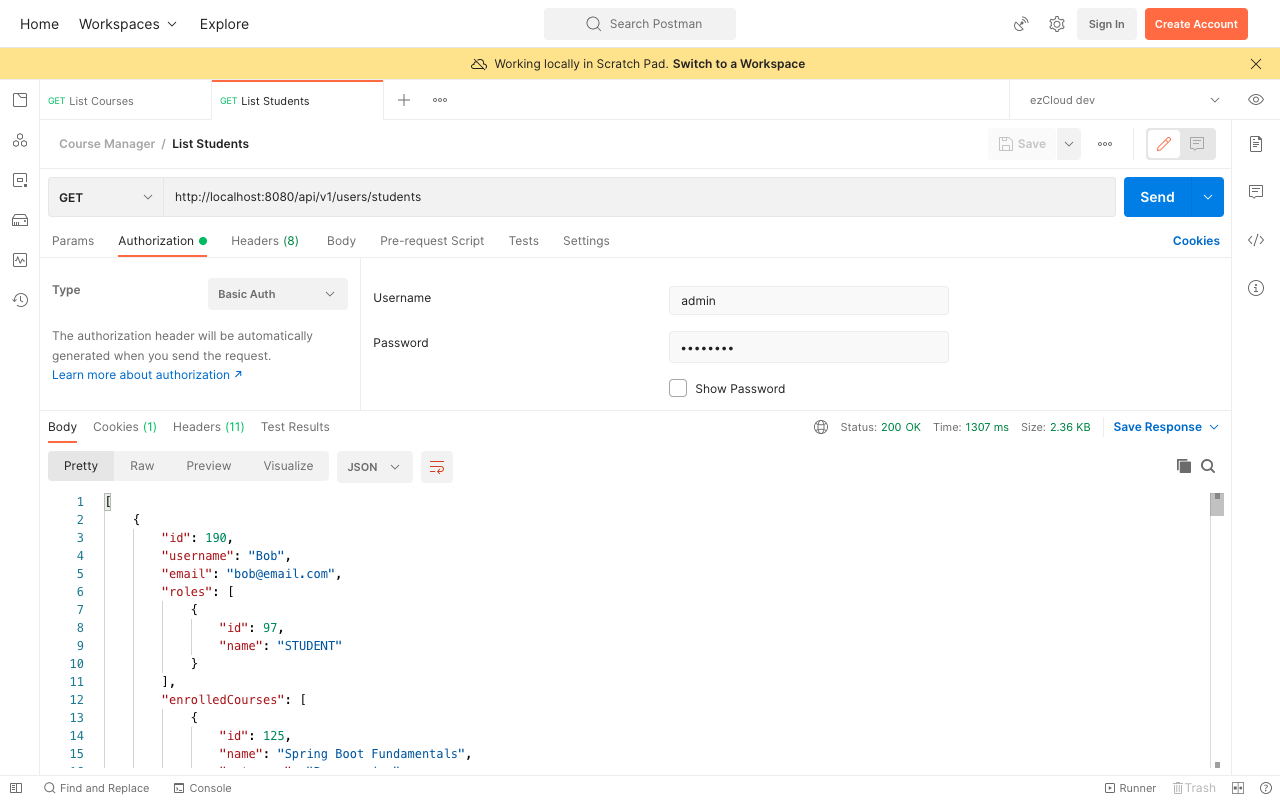
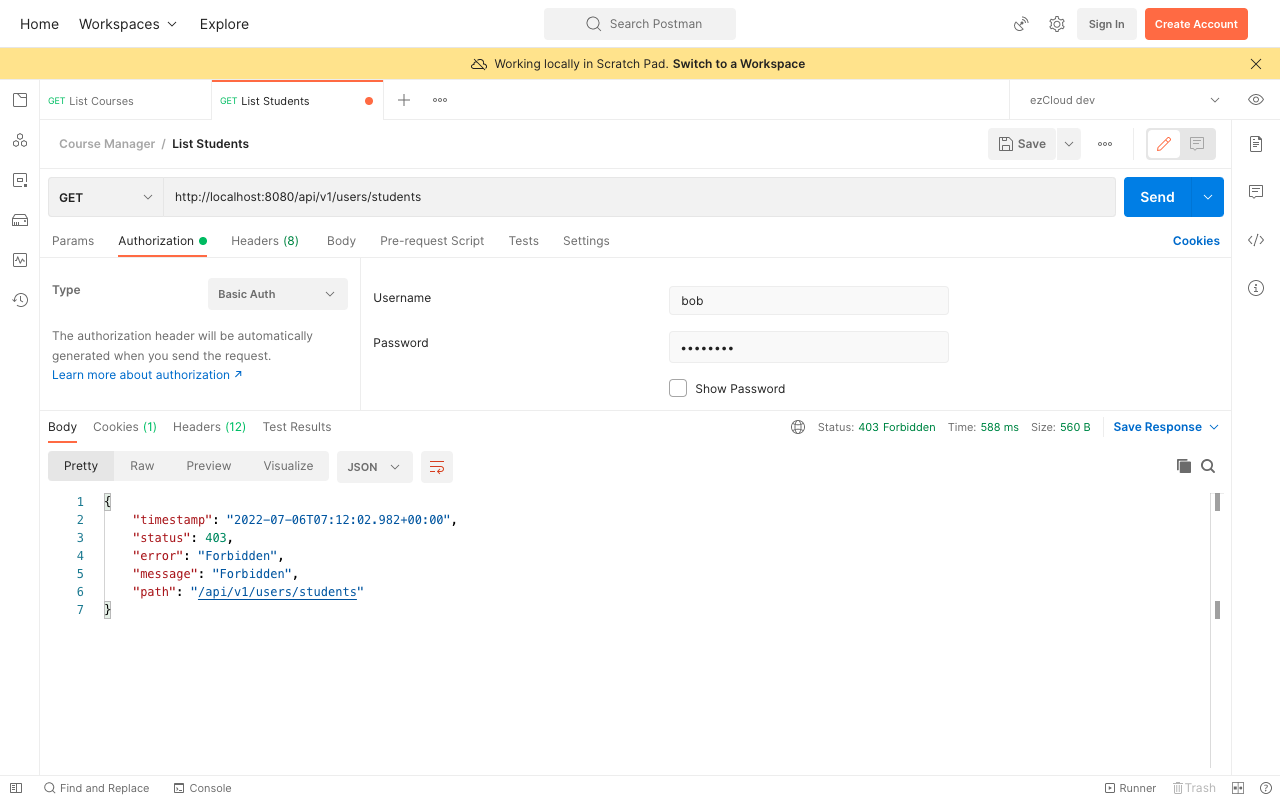
If we access the ListStudents API using Admin user after restarting the application, we can see the list of students as response. But if we access the same API using Bob who does not have ADMIN role, we will get 403 Forbidden error now.
Note
Both roles() and authorities() populates the authorities in User class, as it has no specific attribute to hold the roles information. But roles() automatically prefixes each entry with ROLE_. This means builder.roles("ADMIN") is equivalent to builder.authorities("ROLE_ADMIN").
Therefore we should never call them both on UserBuilder because the latter will always override the authorities set by the former. Here we are intentionally calling roles() after authorities() in order to override the Collections.EMPTY_SET.
There will be scenarios where you would want to set both roles and authorities. In such cases it is always preferable to pass the roles as argument to authorities() method, where each role must be explicitly prefixed with ROLE_ by yourself. We will see this in action in the upcoming chapters.